Synthetic indices trading have emerged as a popular alternative for traders seeking flexibility and unique opportunities in the financial markets. This comprehensive guide will explore what synthetic indices are, how they function, the benefits and risks associated with them, effective trading strategies, and tips for choosing the right broker.
Learn the Secret of Forex Trading, Click here to download a free e-book now
What are Synthetic Indices?
Synthetic indices are financial instruments created to simulate the real market dynamics and volatility. Unlike traditional indices, which are based on actual assets like stocks or commodities, synthetic indices derive their value from predetermined formulas or random number generation. This allows them to mimic the behavior of real-world markets without being directly influenced by external events.
How Do Synthetic Indices Work?
- Diverse Underlying Assets:
Synthetic indices incorporate various underlying assets, including currencies, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. This diversity helps create an index that reflects broader market trends.
- Price Feed:
The value of synthetic indices is continuously updated based on real-time price feeds from these underlying assets, ensuring that traders have access to the latest market information.
- 24/7 Trading:
One of the key advantages of synthetic indices is their availability for trading around the clock, unlike traditional stock markets that have specific operating hours.
-
Leverage:
Traders can often use leverage when trading synthetic indices, allowing them to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. However, this also increases the potential for both gains and losses.
Benefits of Trading Synthetic Indices
-
Accessibility:
Synthetic indices trading typically have lower barriers to entry compared to traditional markets, making it easier for new traders to participate.
-
Controlled Environment:
Since synthetic indices are not tied to real-world assets, they provide a more controlled trading environment. This allows traders to develop and test strategies without the unpredictability of actual market events.
-
Reduced Market Manipulation Risks:
The algorithmic nature of synthetic indices reduces the likelihood of market manipulation compared to traditional markets
Risks Involved in Synthetic Indices Trading
While synthetic indices offer unique opportunities, they also come with specific risks:
-
Volatility:
The prices of synthetic indices can be highly volatile, leading to rapid price swings that can result in significant gains or losses.
-
Leverage Risks:
While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases potential losses. Traders must manage their leverage carefully to avoid substantial financial setbacks.
-
Market Knowledge Requirement:
A solid understanding of the underlying assets and market dynamics is essential for successful trading in synthetic indices.
Choosing the Right Broker
Selecting a reputable broker is crucial for successful synthetic indices trading; Consider the following factors when selecting a broker for synthetic indices:
-
Regulation and Reputation:
Ensure that your chosen broker is well-regulated and has a solid reputation within the trading community.
-
Trading Platform Features:
Look for brokers that offer user-friendly platforms with essential tools for analysis and trade execution.
-
Fees and Commissions:
Compare fees across different brokers to find one that offers competitive rates without compromising service quality.
Effective Trading Strategies for Synthetic Indices
Trading synthetic indices can be both exciting and challenging due to their unique characteristics. To enhance your trading success, it’s essential to adopt effective strategies tailored to the nature of these indices. Below are several proven strategies that can help you navigate the synthetic indices market effectively.
Trend Following
Trend following is a powerful trading strategy that allows traders to capitalize on the momentum of price movements in synthetic indices. By identifying and riding trends, traders can improve their chances of making profitable trades. This section will delve deeper into how to identify trends, particularly using candlestick patterns, which are vital for visualizing market sentiment and potential price movements.
- Identifying Trends
In trading, a trend refers to the general direction in which the price of an asset is moving. Trends can be classified into three categories:
- Uptrend: Characterized by higher highs and higher lows.
- Downtrend: Defined by lower highs and lower lows.
- Sideways Trend: Occurs when prices move within a horizontal range without establishing a clear direction.
Using Candlestick Patterns to Identify Trends
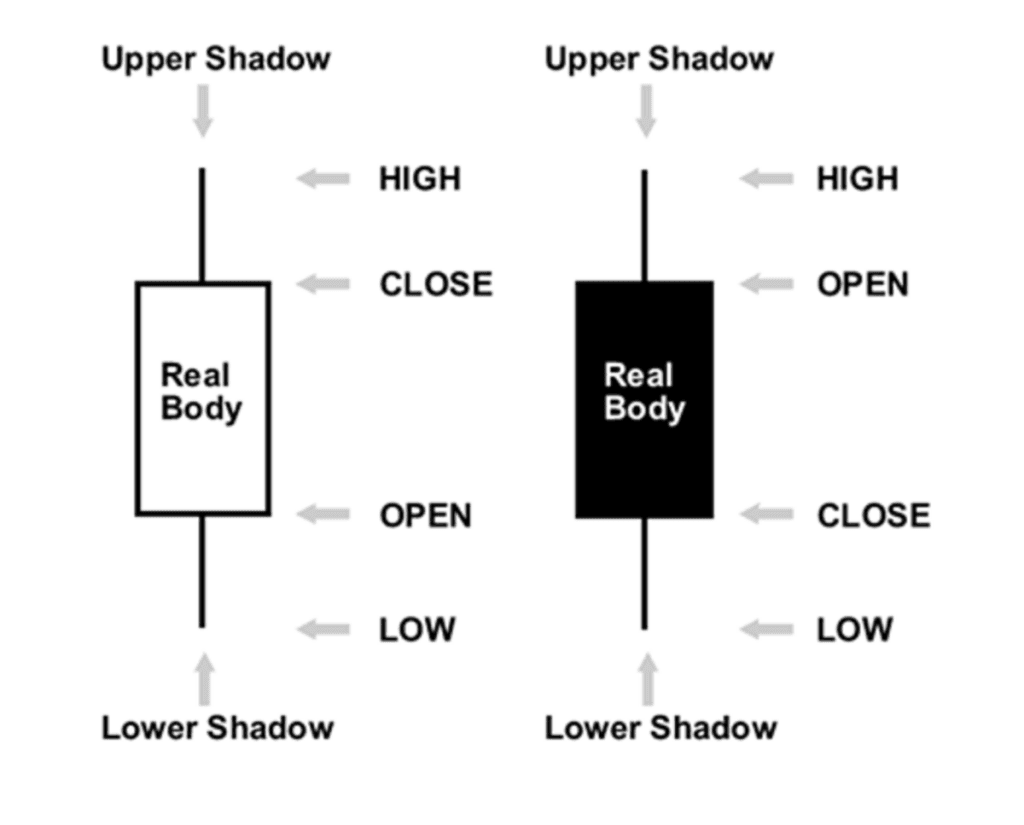
Candlestick patterns are essential tools for traders looking to identify trends and potential reversals. Each candlestick provides information about the opening, closing, high, and low prices over a specific period, allowing traders to gauge market sentiment. Here are some key candlestick patterns that can help identify trends:
- Hammer and Hanging Man
- Hammer: This bullish reversal pattern forms at the end of a downtrend. It has a small body at the upper end of the trading range and a long lower shadow, indicating that buyers pushed prices back up after sellers drove them down.
- Hanging Man: This bearish reversal pattern appears at the end of an uptrend and has a similar shape to the hammer. However, it signals potential weakness as sellers have pushed prices down significantly during the session.
- Engulfing Patterns
- Bullish Engulfing:
This pattern occurs when a small bearish candle is followed by a larger bullish candle that completely engulfs it. It indicates strong buying pressure after a downtrend and suggests that the trend may reverse upward.
- Bearish Engulfing:
Conversely, this pattern appears at the end of an uptrend when a small bullish candle is engulfed by a larger bearish candle. It signals that sellers have taken control, potentially leading to a downward trend.
- Doji Candlesticks
A doji candlestick has very little body and indicates indecision in the market. When it appears after an uptrend or downtrend, it can signal a potential reversal:
- Gravestone Doji: Found at the top of an uptrend, suggesting that buyers are losing momentum.
- Dragonfly Doji: Occurs at the bottom of a downtrend, indicating potential bullish reversal as buyers begin to regain control.
- Morning Star and Evening Star
- Morning Star: This three-candle pattern consists of a bearish candle followed by a small-bodied candle (doji) and then a bullish candle. It indicates that after a downtrend, buyers are starting to take control.
- Evening Star: The opposite of the morning star, this pattern appears after an uptrend and consists of a bullish candle followed by a doji and then a bearish candle. It suggests that sellers are gaining strength.
Combining Candlestick Patterns with Other Indicators
While candlestick patterns provide valuable insights into market trends, combining them with other technical indicators can enhance their effectiveness:
- Moving Averages: Using moving averages can help confirm trends identified by candlestick patterns. For example, if a bullish engulfing pattern occurs above a moving average line, it strengthens the case for an upward trend.
- Volume Analysis: High trading volume accompanying candlestick patterns can indicate stronger signals. For instance, if a hammer forms with high volume, it suggests strong buying interest.
Practical Steps for Trend Following Using Candlestick Patterns
Analyze Higher Timeframes: Start by identifying trends on higher timeframes (e.g., daily or weekly charts) to understand the overall market direction.
Look for Candlestick Patterns: Zoom into lower timeframes (e.g., hourly or 15-minute charts) to spot specific candlestick patterns that signal potential entry points aligned with the identified trend.
Confirm with Indicators: Use additional technical indicators like moving averages or RSI (Relative Strength Index) to confirm your findings before entering trades.
Set Entry and Exit Points: Determine your entry point based on confirmed patterns and set stop-loss orders to manage risk effectively.
Monitor Market Conditions: Keep an eye on economic news or events that may impact market sentiment and influence trends.
Breakout Trading
Breakout trading is a popular strategy that allows traders to capitalize on significant price movements when an asset breaks out of its established support or resistance levels. For beginners, understanding how to identify breakouts and the key elements to look for is crucial for successful trading. This guide will explain the fundamentals of breakout trading, how to spot potential breakouts, and what to consider before entering a trade.
What is a Breakout?
A breakout occurs when the price of an asset moves outside its defined trading range, typically above resistance or below support levels. This movement often signifies the beginning of a new trend, either bullish (upward) or bearish (downward). Traders aim to enter positions early in this new trend to maximize potential profits.
How to Identify a Breakout
Identifying a breakout involves several steps and tools. Here’s how newbies can effectively spot potential breakouts:
- Understand Support and Resistance Levels
- Support Level: This is the price level at which an asset tends to stop falling and may bounce back up due to increased buying interest.
- Resistance Level: Conversely, this is where the price tends to stop rising and may reverse due to increased selling pressure.
To identify these levels, traders can look at historical price charts and mark areas where the price has repeatedly bounced off or been rejected.
- Look for Consolidation Patterns
Before a breakout occurs, prices often consolidate within a narrow range. This phase indicates indecision in the market, where buyers and sellers are in equilibrium. Common consolidation patterns include:
- Triangles: Formed by converging trendlines.
- Rectangles: Horizontal ranges where prices oscillate between support and resistance.
- Flags and Pennants: Short-term continuation patterns that indicate brief pauses before the trend resumes.
Recognizing these patterns can help traders anticipate breakouts.
- Monitor Volume
Volume plays a critical role in confirming breakouts. A breakout accompanied by high trading volume indicates strong interest and conviction in the price movement. Conversely, low volume during a breakout may suggest a false breakout (or “fakeout”), where the price quickly reverses after breaking out of its range.
- Use Technical Indicators
In addition to candlestick patterns, traders can utilize various technical indicators to validate potential breakouts:
- Moving Averages: Help smooth out price data and identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Indicates overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: Show volatility and can help identify breakout points when prices move outside the bands.
Key Candlestick Patterns for Breakout Trading
Candlestick patterns provide visual cues about market sentiment and potential breakout points. Here are some important candlestick patterns to watch for:
- Bullish Engulfing Pattern: A small bearish candle followed by a larger bullish candle that engulfs it, signaling strong buying pressure.
- Bearish Engulfing Pattern: A small bullish candle followed by a larger bearish candle that engulfs it, indicating selling pressure.
- Doji Candlestick: Indicates indecision; if it appears near support or resistance levels, it could signal an impending breakout.
Things to Look Out For When Trading Breakouts
When engaging in breakout trading, consider these essential factors:
- Confirm the Breakout
Before entering a trade, wait for confirmation that the breakout is legitimate. This may involve waiting for additional candlesticks to close beyond the support or resistance level with increased volume.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders
To manage risk effectively, place stop-loss orders just below the broken resistance level for bullish breakouts or above the broken support level for bearish breakouts. This helps protect your capital in case of false breakouts.
- Define Profit Targets
Establish clear profit targets based on previous price movements or technical analysis. A common method is to measure the height of the consolidation pattern and project it in the direction of the breakout.
- Be Aware of Market Conditions
External factors such as economic news releases or geopolitical events can impact market sentiment and lead to volatility around breakout points. Stay informed about upcoming events that may affect your trades
Range Trading
Range trading is a popular strategy that allows traders to capitalize on price movements within a defined range, characterized by established support and resistance levels. This approach is particularly effective in markets that exhibit sideways price action, where the asset oscillates between two price points without a clear trend.
What is a Trading Range?
A trading range occurs when the price of an asset consistently fluctuates between a high resistance level and a low support level over a specific period. Traders identify these levels to make informed decisions about when to enter or exit trades.
- Support Level: The lower boundary where buying interest tends to emerge, preventing the price from falling further.
- Resistance Level: The upper boundary where selling pressure typically arises, preventing the price from rising higher.
How to Identify a Trading Range
To effectively engage in range trading, traders must first identify the trading range:
- Look for Consistent Highs and Lows: A valid trading range is established when the price has bounced off the same support and resistance levels at least twice.
- Use Technical Indicators: Tools like moving averages, Bollinger Bands, or oscillators (e.g., RSI) can help confirm overbought or oversold conditions within the range.
- Volume Analysis: Monitoring trading volume can provide insights into the strength of the support and resistance levels. A significant increase in volume during a bounce off these levels can indicate strong buying or selling interest.
Strategies for Range Trading
Once a trading range is identified, traders can employ several strategies:
- Buying Near Support: Enter long positions when the price approaches the support level, anticipating a rebound back toward the resistance level.
- Selling Near Resistance: Enter short positions when the price nears the resistance level, expecting it to drop back down toward support.
- Limit Orders: Traders can use limit orders to automatically enter positions at predetermined levels of support or resistance, ensuring they capitalize on price movements without needing to monitor the market continuously.
Key Considerations for Range Trading
While range trading can be profitable, traders should be aware of certain factors:
- Risk Management: Set stop-loss orders just outside the established support or resistance levels to minimize potential losses in case of false breakouts.
- Market Conditions: Be cautious during periods of high volatility or significant news events that may lead to breakouts from established ranges.
- Watch for Breakouts: A breakout occurs when the price moves outside the defined range, signaling a potential new trend. Traders should confirm breakouts with increased volume and consider waiting for a retracement before entering new positions.
Risk Management Tools
Effective risk management is crucial when trading synthetic indices due to their inherent volatility.
- How It Works: Utilize tools such as stop-loss and take-profit orders to protect your capital. Setting realistic profit targets and defining acceptable risk levels for each trade can help manage potential losses.
- Benefits: Proper risk management helps safeguard your trading account from significant drawdowns and emotional decision-making during volatile periods.
Practice with a Demo Account
Before committing real capital, practicing with a demo account is invaluable for developing your trading skills and strategies.
How It Works: Most brokers offer demo accounts where traders can practice without risking real money. This allows you to familiarize yourself with different synthetic indices and test various strategies in real-time market conditions.
Benefits: Gaining experience in a risk-free environment helps build confidence and refine your approach before transitioning to live trading.
Keep a Trading Journal
Maintaining a trading journal is an effective way to track your performance and learn from your experiences.
How It Works: Record details of each trade, including entry and exit points, reasons for taking the trade, outcomes, and emotions experienced during the trade.
Benefits: Reviewing your journal regularly helps identify patterns in your trading behavior, enabling you to make informed adjustments to your strategy over time.
Conclusion
Synthetic indices trading provides a unique opportunity for traders looking to explore new avenues in financial markets. By understanding how these instruments work, recognizing their benefits and risks, employing effective strategies, and choosing a reliable broker, traders can enhance their chances of success in this innovative trading landscape. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, synthetic indices offer a flexible platform for honing your skills and diversifying your portfolio.
Risk Disclaimer
Deriv offers complex derivatives, such as options and contracts for difference (“CFDs”). These products may not be suitable for all clients, and trading them puts you at risk. Please make sure that you understand the following risks before trading Deriv products: a) you may lose some or all of the money you invest in the trade, b) if your trade involves currency conversion, exchange rates will affect your profit and loss. You should never trade with borrowed money or with money that you cannot afford to lose.